Sous BSD, il est possible d’utiliser le paquet unbound pour disposer d’un relais ou d’un serveur DNS local. Cette bidouille concerne la distribution pfSense (FreeBSD) qui dispose nativement de cette fonctionnalité. En revanche, côté monitoring, il n’y a pas grand chose de natif! Voici donc comment surveiller le serveur DNS unbound avec Munin.
Il faut d’abord s’assurer de disposer de munin-node sur la passerelle pfSense. Cette bidouille est détaillée ici.
Les plugins munin pour unbound ne sont malheureusement pas installés lors du déploiement du paquet munin-node. Il faut donc les installer manuellement. Rien de bien méchant!
Il faut commencer par télécharger les sources du paquet unbound depuis le site dédié: https://unbound.net/download.html
Ensuite, il faut copier le fichier unbound-x.x.x.tar.gz sur le serveur pfSense et le décompresser:
[2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: pkg update [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: pkg install wget [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: rehash [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: wget https://www.unbound.net/downloads/unbound-1.5.8.tar.gz [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: tar -xvf unbound-1.5.8.tar.gz
Une fois décompressé, il faut copier le plugin Munin pour unbound dans le répertoire des plugins munin-node et le rendre utilisable par munin-node. On peut ensuite supprimer les sources du paquet unbound:
[2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: cp unbound-1.5.8/contrib/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/ [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: chmod +x /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: chown munin:munin /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: rm -rf /root/unbound-1.5.8*
Une fois le plugin situé au bon endroit, il suffit d’activer les différentes statistiques disponibles pour ce plugin:
[2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_by_class [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_by_flags [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_by_opcode [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_by_rcode [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_by_type [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_histogram [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_hits [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_memory [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: ln -s /usr/local/share/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_ /usr/local/etc/munin/plugins/unbound_munin_queue
Dans /usr/local/etc/munin/plugin-conf.d/plugins.conf, rajouter ceci:
[unbound*] user root env.statefile /var/munin/plugin-state/unbound-state env.unbound_conf /var/unbound/unbound.conf env.unbound_control /usr/local/sbin/unbound-control env.spoof_warn 1000 env.spoof_crit 100000
Vérifier ensuite la présence des ces options dans /var/unbound/unbound.conf:
# Statistics # Unbound Statistics statistics-interval: 0 extended-statistics: yes statistics-cumulative: yes
Pour terminer cette bidouille, relancer le client munin-node:
[2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: /usr/local/etc/rc.d/munin-node stop [2.2.5-RELEASE][root@pfSense]/root: /usr/local/etc/rc.d/munin-node start
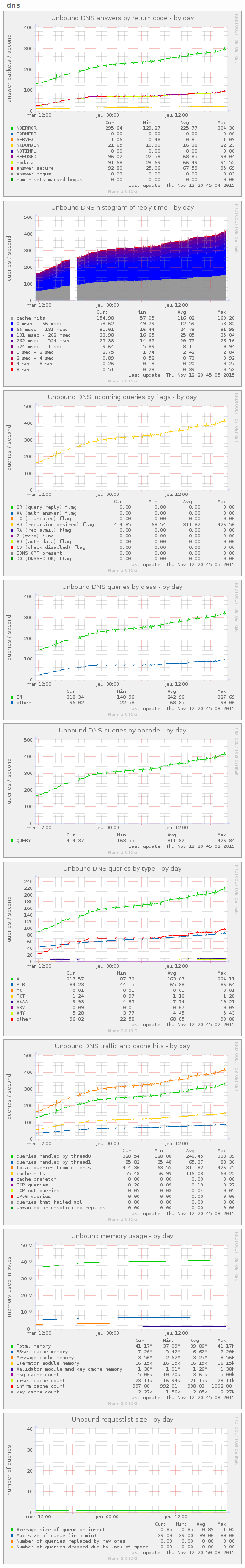
Il devrait être possible au bout de 5 minutes de voir plusieurs nouveaux graphiques dans l’interface Web de Munin. Au bout de quelques heures, ça donne ceci: